An Update on Surgical Robotics
It’s been a rough two years for the surgical robotics market. Intuitive is still the 800-pound gorilla in the room, but the entire market segment, nevertheless, struggles to prove its value and justify its high cost for capital equipment and single-use devices—often proprietary to each robot manufacturer.
Why This Is Important
Intuitive Surgical still dominates the market. The executive team promised procedure growth and delivered 19 percent,1 well above analyst projections. Even with impressive procedure growth, Intuitive’s shares dropped based on continued low spend for capital equipment at U.S. hospitals combined with global supply chain issues.
Many analysts, like BTIG, were not deterred by Intuitive’s increase in operating expenses, even though investors may run if earnings per share drop. BTIG stated Intuitive’s plan remains consistent and the company is strategically capable of sustaining procedure growth as the economy continues to correct itself over time.1 The CEO of Intuitive Surgical—Gary Guthart—agrees and believes recent growth in procedures was propelled by general surgery in the U.S. Outside of the U.S., use of da Vinci is expanding beyond urology with expansion in oncologic procedures in gynecology, thoracic surgery, and general surgery. He noted the global ecosystem of healthcare was stressed by COVID, which led the way for employment issues, supply challenges, and delays caused by logistics. He also stated, however, an increase in procedure demand would create future requirements for replacement capital equipment sales for new, improved surgical robots in the U.S. In the Intuitive Surgical 1Q22 earnings call, in addition to the use of da Vinci in general surgery in the U.S., it was noted procedure growth was led by cholecystectomy, bariatric, hernia repair, and rectal surgery.2
The installed base of da Vinci systems grew year-over-year to 311 in 1Q22 (Table 1), bringing the clinical installed base to 6,920 systems. The demand for da Vinci capital equipment has been historically uneven and, in the earnings call, Guthart reported that after several quarters of capital growth, Intuitive is seeing lower demand for its capital pipeline in the U.S.2
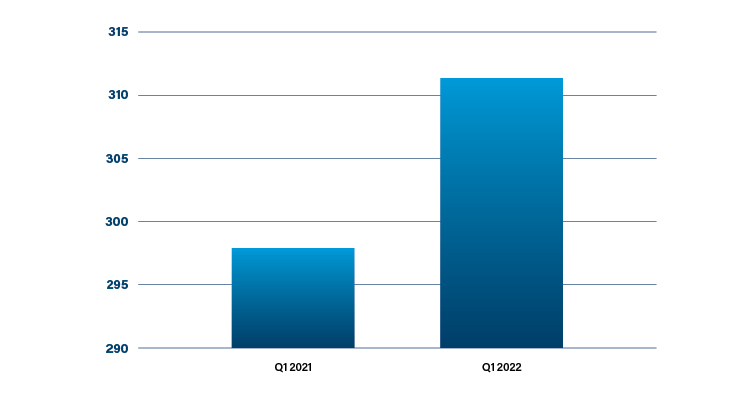
Table 1: da Vinci Systems installed in Q122 vs. Q1212
In the U.S., Intuitive sold 186 systems in 1Q22, which was relatively flat. Outside the U.S., Intuitive sold 125 da Vinci robots in 1Q22, compared with 108 in 1Q21 (Table 2).2
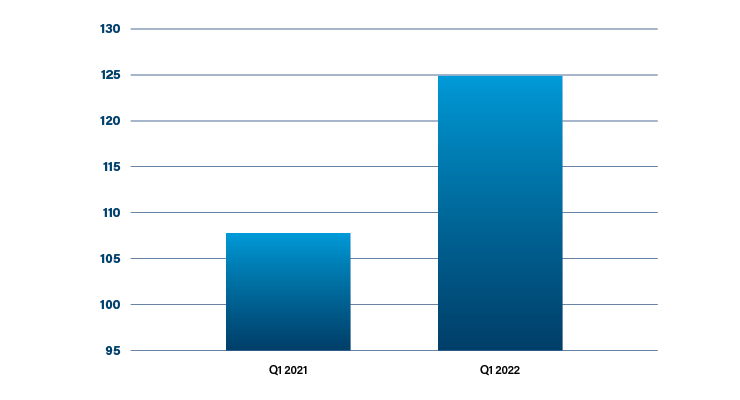
Table 2: OUS da Vinci capital equipment placement2
Better Clinical Outcomes?
Intuitive Surgical and its competitors claim procedures performed with a robot are a better form of surgery and there are many surgeon adherents who claim improved patient outcomes. In a recent metanalysis of 50 randomized controlled trials comparing robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) to traditional laparoscopic methods for abdominal or pelvic procedures, however, it is suggested the clinical advantages of RAS over traditional approaches are limited.
Surgeon RAS advocates believe robots allow more precision during procedures, reduced recovery times, and improved clinical outcomes for patients. In the metanalysis, published in the Annals Of Internal Medicine, 9 percent of laparoscopies reported serious complications requiring an additional surgical intervention as compared to 8 percent of RAS (n=39 studies). In studies of gastrointestinal surgery, critical complications ranged from 0 to 2 percent for RAS and from 0 to 3 percent for laparoscopy (Table 3).3,4
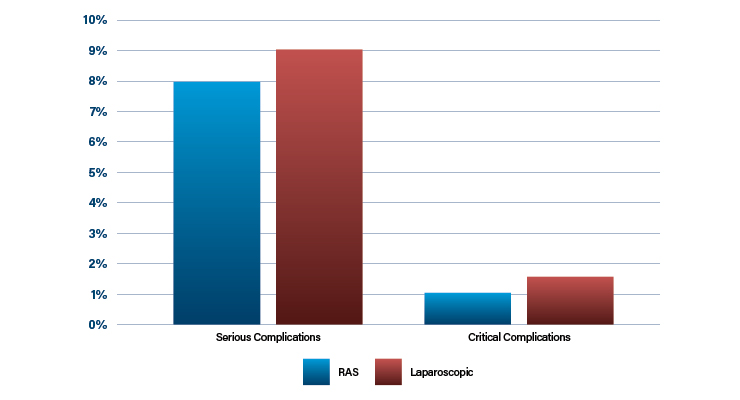
Table 3: Average complication rates between robot-assisted surgeries and laparoscopic procedures3
There are multiple reasons for a surgeon to switch from performing an RAS or laparoscopic procedure to an open surgery. In te Annals Of Internal Medicine study data, this occurred in 8 percent of RAS procedures and 12 percent of laaroscopic procedures.3,4
Eight of the tudies In the metanalysis tracked outcomes for two years and found mortality rates were low—RAS (3 percent), aparoscopy (0 percent), and open surgeries (5 percent).3,4
Other finding included average procedure durations as high as 265 minutes for gynecological RAS, compared with 226 minutes for laparoscopic gynecological procedures and 187 minutes for open GYN procedures. These findings correlated with time studies in urologic and colorectal procedures with RAS surgeries taking longer than laparoscoic and open procedures.3,4
There are ergoomic benefits for surgeons with RAS. OR procedures that can take many hours and require practiced handeye coordination to move laparoscopic devices into the proper position, benefit from robotic procedures. Surgeons who prefer to use the da Vinci robot do so because they believe it offers superior visualization, hand and wrist flexibility, and the ability to be seated during a procedure.5
No article on robotic surgery would be complete, however, without mentioning the much higher cost of RAS over traditional surgical methods. According to a Nature article, in 2003, fewer than 1 percent of U.S. surgeons performed RAS for radical prostatectomies. Adoption was swift. By 2014, RAS had surged to approximately 90 percent of radical prostatectomies, a majority market share almost unheard of. Further, the cost of the da Vinci with full installation is $2 million. Intuitive Surgical’s stock price reflected its dominance in urological surgery and grew 66 percent from $312 in 2017 to $520 in 2019 and total sales grew from $3.7 billion in 2018 to $4.5 billion in 2019.5
The disposable instruments required for RAS are also more expensive. In a study from Columbia, researchers found the median total cost for a RAS oophorectomy was $7,426, while traditional laparoscopic oophorectomy was $4,922. Median total costs for RAS cystectomy was $7,444; compared to a traditional laparoscopic cystectomy that was $4,133.6 Also, researchers found that RAS service contracts and the additional OR time make them so costly that many hospitals cannot afford them.7
The Medi-Vantage Perspective
Many competitors that want a bite of the robotic surgery pie, but COVID and pandemic-induced supply chain issues have been powerful obstacles. New competition will reduce prices, which will then require sophisticated price strategies on the part of Intuitive Surgical’s competition. Of note is J&J’s announcement it won FDA clearance for the Monarch platform for use in endourological procedures.8 This makes the Monarch a true competitor to Intuitive Surgical in urology.
It will be interesting to watch how price strategy will be used by J&J against Intuitive Surgical. Price strategy is critically dependent upon the differentiation that a medical device provider brings to market and the value it brings in reducing costs or improving patient outcomes—values that Intuitive Surgical has never been able to prove. Think of the price premium a true improvement in clinical outcomes could command.
Article source: MDDI










